Limiter Stereo
Detailed: LSP Limiter Stereo (B1S)
Formats: CLAP, JACK, LADSPA, LV2, VST2, VST3
Categories: Limiter
Developer: Vladimir Sadovnikov
Description:
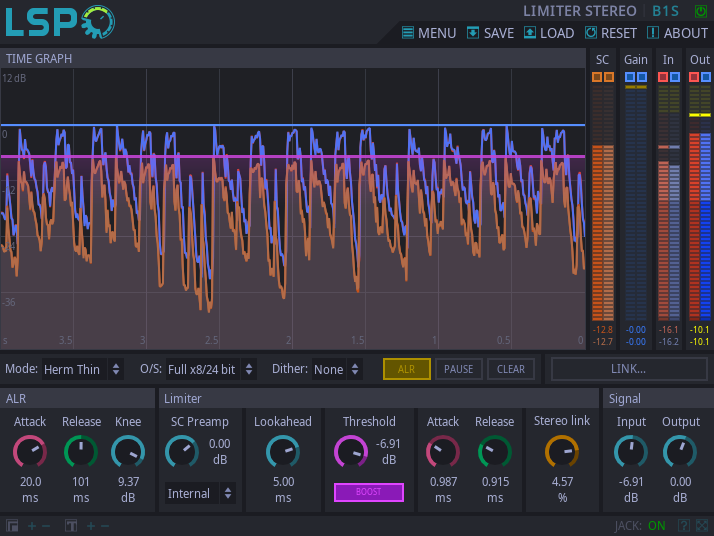
This plugin implements a limiter with flexible configuration. In most cases it acts as a brick-wall limiter but there are several settings for which is acts as an compressor with extreme settings, so the output signal may exceed the limiter's threshold. It prevents input monosignal from raising over the specified Threshold.
Attention: this plugin implements set of limiting modes, most of them are iterative. That means that CPU load may be not stable, in other words: the more work should be done, the more CPU resources will be used. Beware from extreme settings.
The gain reduction algorithm is split into two stages:
- Automated Level Regulation (ALR) which acts like a compressor with infinite ratio for purpose of estimating the smoothed gain reduction level. The gain reduction level is controlled by the envelope of the signal applied to the compressor's gain reduction curve. The smoothness of the envelope is controlled by the Attack and Release knobs in the ALR section. Since different signals have different envelopes with short release time, the Knee knob allows to adjust the threshold of the compressor. Adjusting Knee may give possibility to gain some additional decibels of loudness in the final result.
- Peak cutting algorithm which searches peaks above the threshold values and applies short gain reduction patches to the signal. The form of patch is controlled by the Mode selector and it's length is controlled by the corresponding Attack and Release knobs. Note that Lookahead also affects these values: Attack can not be larger than Lookahead and Release can not be twice larger as Lookahead. Setting these values larger than allowed automatically makes them considered to be set to maximum possible values.
Simplified peak processing example is shown on the following picture:
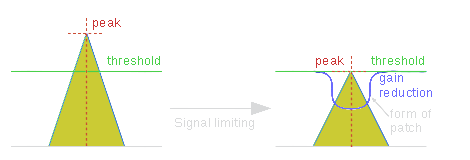
Of course, the output signal does not repeat the envelope form of input signal because it's amplitude is changed smoothly, so in fact the form of output signal is more complicated.
Currently there are three forms of patches applied to the gain curve - hermite (using cubic polynom for interpolation transients), exponential and linear. These forms can be explained with following picture:

Gain reduction patch affects not only the peak sample, but also surrounding samples. The position and form of this interpolation is related to the peak, so there are four different variants of patch envelope - thin, tail, duck and wide. All these forms related to the peak are shown on the following picture:
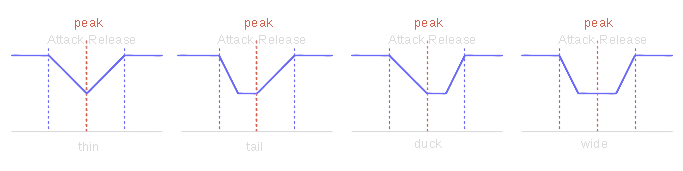
On this image, sloping lines mean the transision part of the patch. The flat cap in the middle before the peak is a half of attack time, the flat cap in the middle after the peak is a half of release time. Also it's obvious that different envelope forms differently affect dynamics of the signal.
Controls:
- Bypass - bypass switch, when turned on (led indicator is shining), the plugin bypasses signal.
- Pause - pauses any updates of the limiter graph.
- Clear - clears all graphs.
- Mode - the selected mode to use by limiter:
- Herm Thin, Herm Wide, Herm Tail, Herm Duck - hermite-interpolated cubic functions are used to apply gain reduction.
- Exp Thin, Exp Wide, Exp Tail, Exp Duck - exponent-interpolated functions are used to apply gain reduction.
- Line Thin, Line Wide, Line Tail, Line Duck - linear-interpolated functions are used to apply gain reduction.
- O/S - oversampling mode:
- None - oversampling is not used.
- Half 2x/16 bit - 2x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 2x/24 bit - 2x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 3x/16 bit - 3x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 3x/24 bit - 3x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 4x/16 bit - 4x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 4x/24 bit - 4x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 6x/16 bit - 6x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 6x/24 bit - 6x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 8x/16 bit - 8x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Half 8x/24 bit - 8x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 2x/16 bit - 2x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 2x/24 bit - 2x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 3x/16 bit - 3x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 3x/24 bit - 3x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 4x/16 bit - 4x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 4x/24 bit - 4x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 6x/16 bit - 6x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 6x/24 bit - 6x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 8x/16 bit - 8x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 16-bit precision of output samples.
- Full 8x/24 bit - 8x Lanczos oversampling of Sidechain signal and Input signal with 24-bit precision of output samples.
- Dither - allows to enable dithering for the specified sample bitness.
- Link - the name of the shared memory link to pass sidechain signal.
- SC - enables drawing of sidechain input graph and corresponding level meter.
- Gain - enables drawing of gain amplification line and corresponding amplification meter.
- In - enables drawing of limiter's input signal graph and corresponding level meter.
- Out - enables drawing of limiter's output signal graph and corresponding level meter.
'ALR' section:
- Attack - allows to control how the raise of the input signal affects the ALR envelope curve. The more value, the more quickly the envelope goes to it's maximum.
- Release - allows to control how the fall of the input signal affect the ALR envelope curve. The more value, the more quickly the envelope goes to it's minimum.
- Knee - allows to control the threshold of the ALR gain curve and, in fact, adjust the balance between two gain reduction stages. Raising the value delegates more work to the peak-cutting algorithm. Lowering the value delegates more work to the ALR gain reduction algorithm.
'Limiter' section:
- SC Preamp - sidechain pre-amplification gain.
- Sidechain Mode - sidechain mode:
- Internal - the input signal is processed as sidechain signal.
- Link - sidechain input is passed by shared memory link.
- Lookahead - the size of lookahead buffer in milliseconds. Forces the limiter to add the corresponding latency to output signal.
- Threshold - the maximum input level of the signal allowed by limiter.
- Boost - applies corresponding to the Threshold gain to the output signal.
- Attack - the attack time of the limiter. Can not be greater than Lookahead time (greater values are truncated) for some modes.
- Release - the attack time of the limiter. Can not be twice greater than Lookahead time (greater values are truncated) for some modes.
'Signal' section:
- Input - overall input signal gain adjustment.
- Output - overall output signal gain adjustment.